
TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Chemokine scavenger D6 is expressed by trophoblasts and aids the survival of mouse embryos transferred into allogeneic recipients. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the diversity of trophoblast subtypes and patterns of differentiation in the human placenta. Integrative single-cell and cell-free plasma RNA transcriptomics elucidates placental cellular dynamics. The structure of the human placenta: implications for initiating and defending against virus infections.
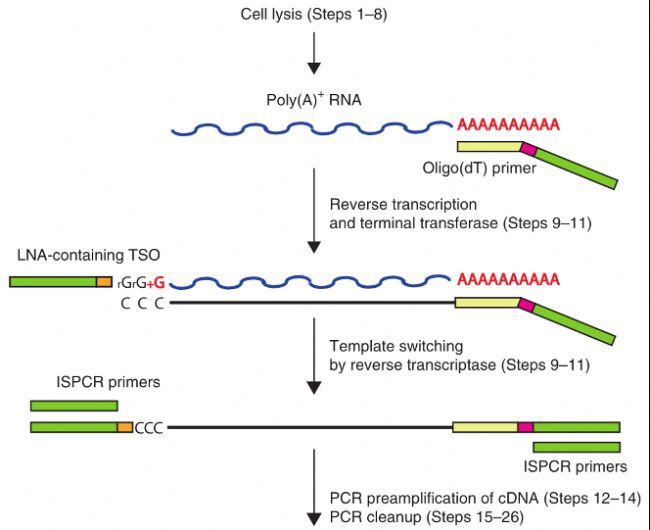
Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Co-evolution of NK receptors and HLA ligands in humans is driven by reproduction. Variable NK cell receptors and their MHC class I ligands in immunity, reproduction and human evolution. Killer Ig-like receptor expression in uterine NK cells is biased toward recognition of HLA-C and alters with gestational age. Human leucocyte antigen (HLA) expression of primary trophoblast cells and placental cell lines, determined using single antigen beads to characterize allotype specificities of anti-HLA antibodies. Placenta accreta spectrum: a need for more research on its aetiopathogenesis. Why is placentation abnormal in preeclampsia? Am. Rheological and physiological consequences of conversion of the maternal spiral arteries for uteroplacental blood flow during human pregnancy. Endometrial glands as a source of nutrients, growth factors and cytokines during the first trimester of human pregnancy: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Hempstock, J., Cindrova-Davies, T., Jauniaux, E. Uterine glands provide histiotrophic nutrition for the human fetus during the first trimester of pregnancy. Human decidual natural killer cells are a unique NK cell subset with immunomodulatory potential. Endometrial decidualization: of mice and men. Our single-cell atlas of the maternal–fetal interface reveals the cellular organization of the decidua and placenta, and the interactions that are critical for placentation and reproductive success.
Our data identify many regulatory interactions that prevent harmful innate or adaptive immune responses in this environment. We develop a repository of ligand–receptor complexes and a statistical tool to predict the cell-type specificity of cell–cell communication via these molecular interactions.
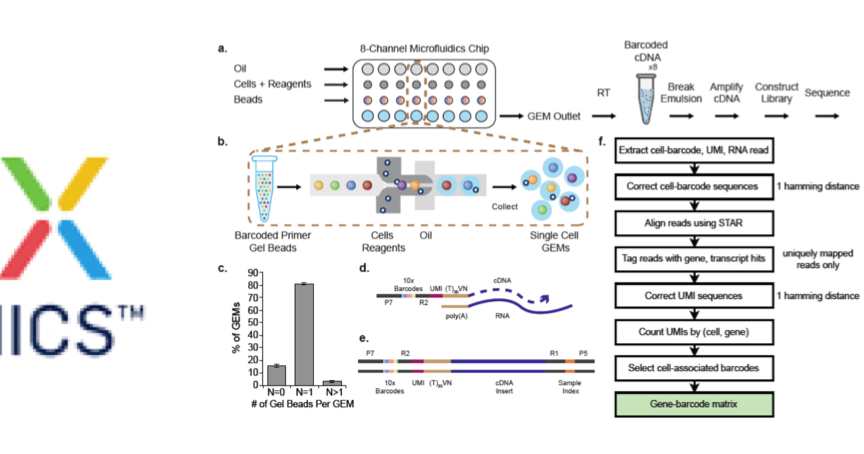
There are three major subsets of decidual natural killer cells that have distinctive immunomodulatory and chemokine profiles. The cellular composition of human decidua reveals subsets of perivascular and stromal cells that are located in distinct decidual layers. Here we profile the transcriptomes of about 70,000 single cells from first-trimester placentas with matched maternal blood and decidual cells.

Trophoblast–decidual interactions underlie common diseases of pregnancy, including pre-eclampsia and stillbirth. During early human pregnancy the uterine mucosa transforms into the decidua, into which the fetal placenta implants and where placental trophoblast cells intermingle and communicate with maternal cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
